Top 5 Node.js Backend frameworks for 2024
Top highlight
Introduction
Node.js has been the talk of town since 2009 and most of the backend developers tend to go for Node.js. Its popularity has been increased over the past few years.
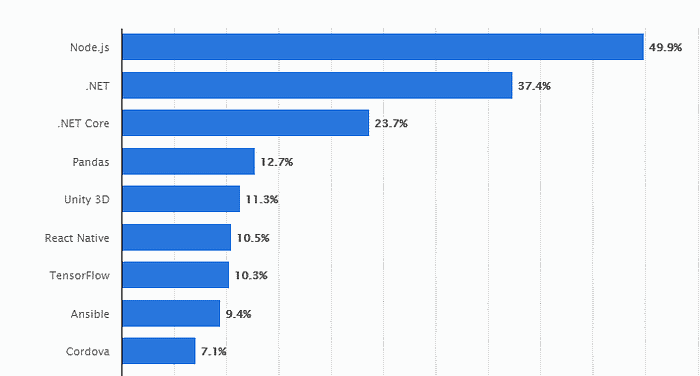
It is known as the most popular web development tool in USA including clients like Netflix and PayPal.
The reason for the increase in popularity is the reduction in loading time and performance improvements. Therefore, it is crucial to analyze the top 5 Node.js Backend frameworks for 2024.
Hence, this article will cover the top 5 Node.js backend frameworks for 2024, their features, and common use cases.
Pst, if you want to check out a simple demo to build an Express API, checkout my Bit Scope.
Express.js: The Tested Champion

Express.js is one of the most famous backend frameworks of Node.js. It is an open-source web application framework, freely available and built upon the Node.js platform. Since it’s a minimal framework, both novice and seasoned web developers tend to go for Express.js. It is mainly used for creating web applications and RESTful APIs.
Key Features: What Makes It Stand Out?
1. Efficient Routing
Express.js offers a clean and simple method for managing various HTTP requests and assigning them to particular tasks. Let’s look at an example.
// app.js
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const port = 3000;
// Route for Homepage
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Welcome to the homepage!');
});
// Route 2
app.get('/user/:id', (req, res) => {
const userId = req.params.id;
res.send(User Profile Page - ID: ${userId} );
});2. Middleware Support
Express.js allows middleware support for handling HTTP requests. Let’s look at a simple example of creating a middleware for logging HTTP request details.
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const port = 3000;
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log(\[${new Date().toLocaleString()}\] ${req.method} ${req.url} );
next();
});3. Easy Database Integration
Express.js is database-agnostic. It doesn’t enforce a specific database choice. Developers can choose their preferred database. The ease of integrating databases with Express.js is because of its modular and flexible nature and the rich ecosystem of npm packages that provide database connectivity.
4. Easy to learn
Express.js is known for its simplicity and minimalistic design, making it so easy for developers to learn, especially if they are already familiar with JavaScript and Node.js.
Plus, you can easily get started with Express.js with tools like Bit. If you’ve not used Bit before, it’s a next-generation build system for composable software.
And, if you think about it, Express.js on its own is composable in nature. You can plug and play components at any point in your app.
For example, you can create middleware components that you can plug in and out at any given time.
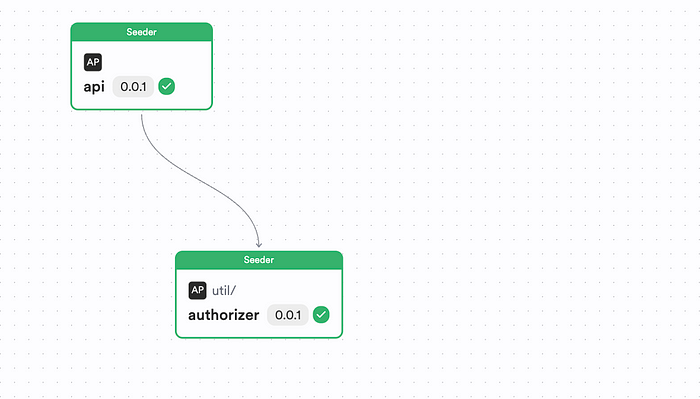
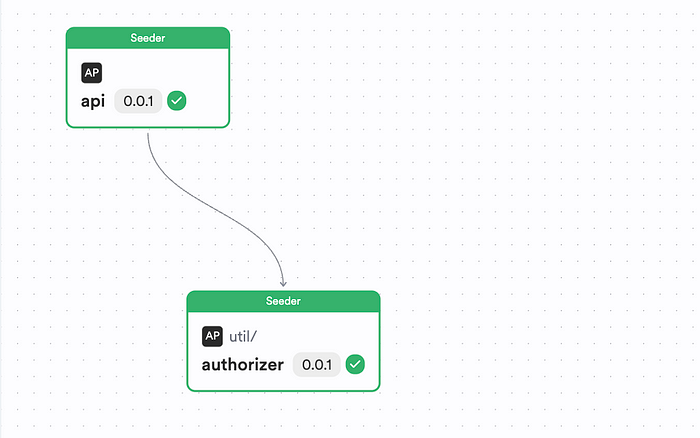
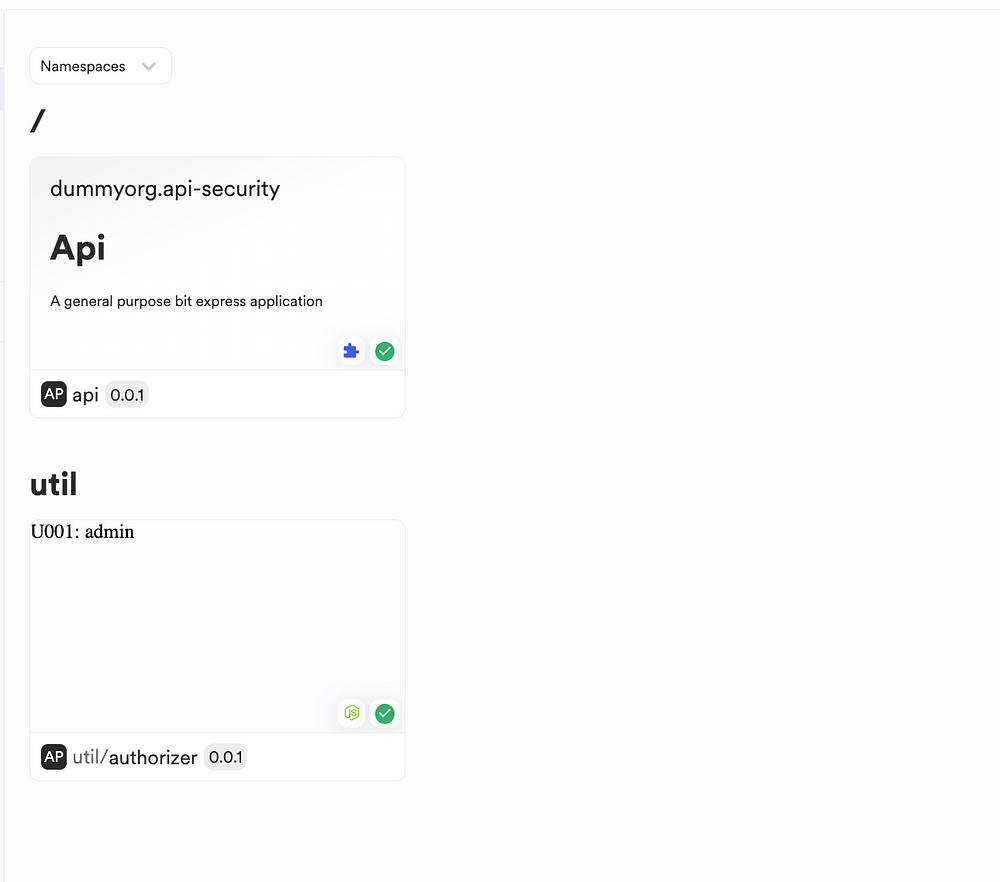
Figure: A Bit Scope of an Express API designed using Bit and Independent Components
You can see two components: an Authorizer as well as an API app. These two components have been implemented as independent Bit components and are maintained and versioned in its isolated space.
By doing so, you’re able to design your app in a composable manner, quickly!
To view this full implementation, check out my Bit Scope.
NestJS: A Modern and Structured Approach

NestJS is a framework that is known for building scalable and efficient Node.js server-side applications. It uses progressive JavaScript and has the capability of writing code in TypeScript. Even though it fully supports Typescript, it can write code in pure JavaScript and includes Object Oriented Programming, Functional Programming, and Functional Reactive Programming.
Key Features: What makes it stand out
1. Modularity
Nest.js allows code to be broken down into separate manageable modules which make it more maintainable. For an example, let’s look at the below module.
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
@Module({
imports: \[
CacheModule
\],
controllers: \[PaymentController\],
providers: \[PaymentService\],
})
export class PaymentModule {}
This payment module can be exported to other modules. In this example, we have exported common cache module inside this module. Since nest.js has a module structure, it makes it easy to maintain.
2. Scalable
Nest.js enables seamless scaling by breaking applications into manageable modules, supporting flexible component replacement, and accommodating high traffic through microservices and asynchronous operations. It ensures efficient handling of increased workload while maintaining reliability.
3. Dependency Injection
Dependency injection is simply the method of adding an external dependency to a class rather than creating it within the class itself. Let’s look at an example.
import {
HttpException, Injectable, NotFoundException
} from '@nestjs/common';
@Injectable()
export class PaymentService {
constructor() {}
getReceipt() {
return 'Payment Receipt';
}
}We have created payment service and added @Injectable() annotation to make it injectable. We can use the created service as stated below.
import { Controller, Get, Post, Body } from '@nestjs/common';
import { PaymentService } from './payment.service';
@Controller('payment')
export class PaymentController {
constructor(private readonly paymentService: PaymentService) {}
@Get()
getPaymentReceipt() {
return this.paymentService.getReceipt();
}
}4. Type Safety
Nest.js uses TypeScript to provide type safety, which can be used to catch potential errors during development and improve code maintainability. Let’s look at an example.
export class PaymentDto {
@IsNotEmpty()
@IsEnum(SERVICE\_PROVIDER\_SLUG, {
message: \`Invalid serviceProvider. Valid options are: ${Object.values(SERVICE\_PROVIDER\_SLUG).join(', ')}\`,
})
serviceProvider: string;
@IsNotEmpty()
@IsNumber()
value: number;
@IsNotEmpty()
@IsString()
validityPeriod: string;
@IsNotEmpty()
@IsArray()
@ArrayNotEmpty()
@ValidateNested()
@Type(() => PaymentAttributesDto)
paymentAttributes: PaymentAttributesDto\[\]
}In this example, we have created a dto that includes multiple parameters and we have added annotations to validate the parameter type. For example, if we send a string value to the “value” parameter, it will throw an error.
Koa.js: Elegant and Lightweight

Koa.js is a smaller, more expressive web framework that is also designed by the Express.js team. It allows you to ditch callbacks and handle errors by leveraging async functions.
Key Features: What makes it stand out
1. Context Object (ctx)
Koa.js includes a functionality called ctx to capture request and response details. This context is passed to each middleware. In this example, we have logged method and request from the ctx object.
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
app.use(async (ctx) => {
const { method, url, request, response } = ctx;
console.log('Method :' + method + ' Request : ' + request);
});
app.listen(3000);2. Middleware Composition
Much similar to Express Js, Koa supports middleware functions for handling HTTP requests and responses. In this example, we have created a simple middleware.
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
await next();
});
app.listen(3000);3. Async/Await Support
Koa uses the async/await syntax for writing asynchronous code in a more synchronous-looking way. The below example consists of using async/await keywords.
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
app.use(async (ctx) => {
const data = await fetchData();
ctx.body = Data: ${data} ;
});
app.listen(3000);4. Error Handling
Koa.Js supports various types of error handling. We can use app.emit() or ctx.throw() to handle errors. The below example consists of mentioned error-handling methods.
const koa = require('koa');
const app = new koa();
//Error Handling Method 1
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
try {
await Promise.reject('Something went wrong');
} catch (err) {
ctx.status = err.status || 500;
ctx.body = err.message;
ctx.app.emit('error', err, ctx);
}
});
//Error Handling Method 2
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
ctx.throw(500, 'error');
});
app.on('error', (err, ctx) => {
console.log(err);
});
app.listen(3000);Hapi.js

Hapi.js which is short for Http-API, is an open-source framework for developing scalable web applications. One of the most basic use cases of hapi is to build REST APIs.
Walmart Labs created hapi js to handle their traffic for events like Black Friday, one of the busiest days for online shopping in the U.S. calendar.
Key Features: What makes it stand out
1. Configuration-Driven Design
Using a configuration object, we are able to configure routes, settings and plugins in Hapi.js.
const Hapi = require('@hapi/hapi');
const server = Hapi.server({
port: 3000,
routes: {
cors: true,
},
});
server.route({
method: 'GET',
path: '/',
handler: (request, h) => {
return 'Hello, Hapi!';
},
});
async function start() {
await server.start();
console.log(Server running at ${server.info.uri} );
}
start();2. Powerful Plugin System
Hapi.js allows plugins to be easily integrated without much hassle. Let’s look at an example.
const start = async function () {
const server = Hapi.server();
await server.register(\[{
plugin: require('plugin1'),
options: {}
}, {
plugin: require('plugin2'),
options: {}
}\]);
};In this example, we have integrated two plugins. Options can be passed to the plugin using options key.
3. Authentication and Authorization
Hapi.js provides built-in support for various authentication strategies and allows developers to define access control policies easily.
server.route({
method: 'GET',
path: '/private-data',
handler: (request, h) => {
// Access private data only if authenticated
const user = request.auth.credentials;
return Welcome, ${user.username}! ;
},
options: {
auth: 'jwt', // Use JWT authentication strategy
},
});Based on the example, we can directly define the authentication strategy as ‘jwt’.
4. Input Validation
Input validation is another crucial aspect of hapi.js. In the options object of a route, we can define which inputs need to be validated. Default validate object consists of below values.
{
headers: true,
params: true,
query: true,
payload: true,
state: true,
failAction: 'error'
}
Adonis.js

Adonis.js is a full-featured MVC framework for Node.js. It has the capability of building scalable and maintainable applications. Adonis.js follows a similar structure to Laravel and includes features like ORM, authentication, and routing out of the box.
Key Features: What makes it stand out
1. Full-stack MVC framework
Adonis.js follows the MVC architectural pattern. Having a MVC framework helps organize code and makes it easier to maintain and scale.
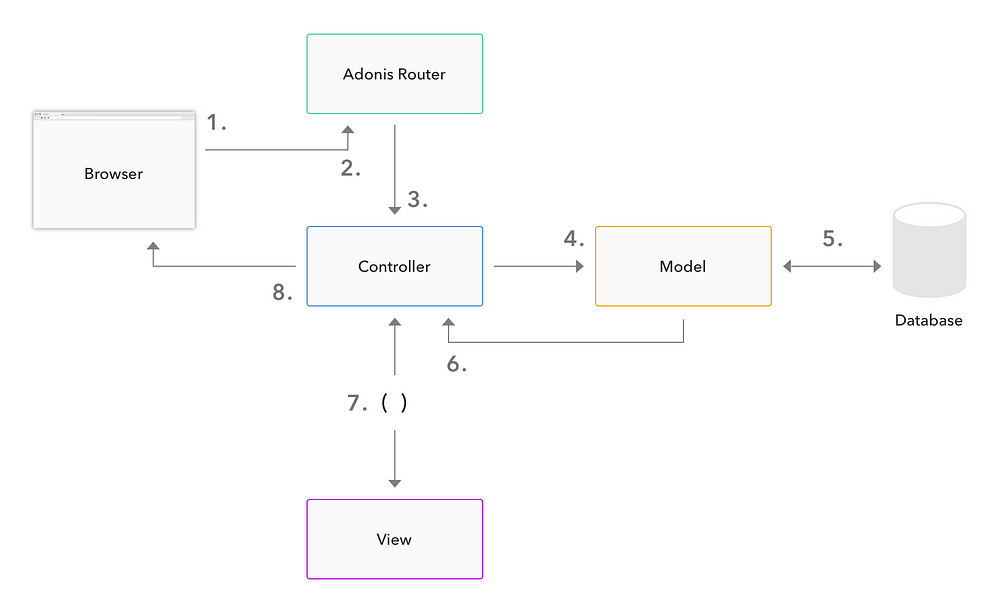
2. Integrated ORM (Lucid) for database interactions
Adonis.js has its own ORM called Lucid. Lucid provides an expressive query builder and supports various database systems. In lucid, we can create models to read and write to the database. Let’s look at the below example.
const Model = use('Model')
class User extends Model {
}
module.exports = User
We are using this user model instead of database queries. Now we are creating a route, where inside we are fetching the users. We can simply user User.all() to fetch the users.
const Route = use('Route')
const User = use('App/Models/User')
Route.get('users', async () => {
return await User.all()
})
3. Authentication system
Adonis.js has built-in support for user authentication and authorization. It provides a set of methods and middleware for handling user sessions, password hashing, and access control.
Conclusion
In 2024, the above-mentioned backend frameworks stand tall in the market.
Whether you chose Express.js for its simplicity, Nest.js for its structure, Adonis.js for productivity, or Koa.js for the elegance, choosing the right framework is crucial.


Comments